Information
The endocannabinoid system of the ECS
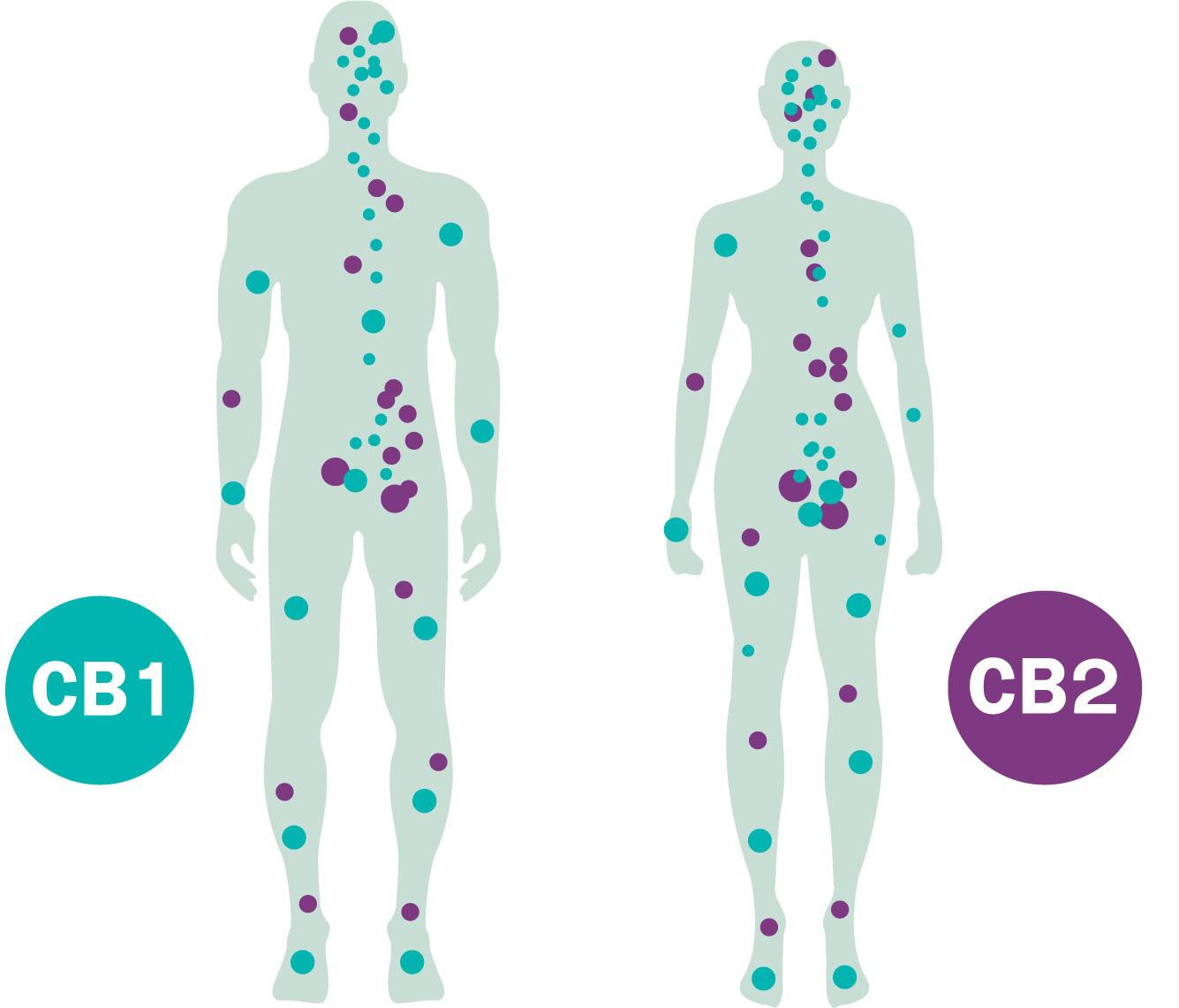
There are many systems in the human body. The endocannabinoid system is relatively recently known and is currently being intensively researched. It consists of endocannabinoids produced by the body – information carriers (key) – and receptors for them – the most numerous are the CB1 and CB2 (lock) receptors, which are distributed in the whole body. Connecting the key with the lock causes a cascade of reactions in the cell and the desired response.
The location of the receptors determines the effect of the action. CB1 receptors are found mainly in the central and peripheral nervous system, but are also abundant in adipose and muscle tissue, liver cells, and the gastrointestinal tract. CB2 is found primarily in tissues related to the immune system – tonsils, spleen, thymus – and on the immune cells themselves – monocytes, B and T lymphocytes, macrophages. They are also found in the nervous system and digestive tract.
What are cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in hemp (phytocannabinoids), but also in the body of all mammals, including humans – we call them endocannabinoids. So far, more than 100 types have been recognized. The best known are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol).
What is CBD?
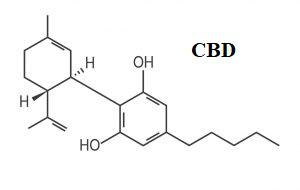
This is short for cannabidiol – one of the main and most famous cannabinoids. CBD has been known since 1940, but the first studies on its effects on the body appeared in the 1970s. Its action appears not only by direct binding to receptors, but also by inhibiting the breakdown of endocannabinoids, which increases their natural level.
What is the effect of CBD on the body?
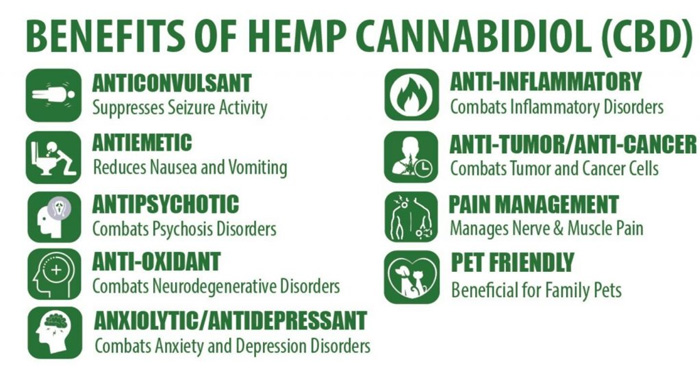
This compound is not psychoactive, does not intoxicate, and does not impair cognitive and motor functions. It has anti–inflammatory, analgesic, anxiolytic, stress–reducing, immunomodulating, improving sleep quality and regenerative effects, reducing painful muscle tension. Moreover, various publications indicate the potential benefits regarding increased cardiovascular risk, insulin resistance, and neurodegenerative disorders. To sum up: it has a holistic effect on the body.
Terpenes and terpenoids
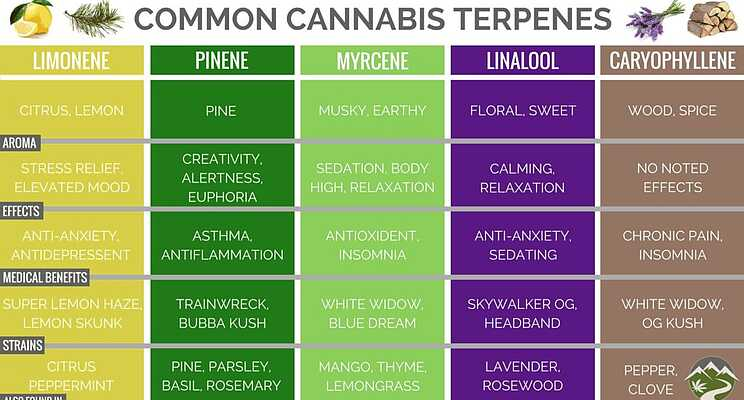
Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are produced – just like cannabinoids – in plant glands – trichomes. They give the characteristic flavor and aroma of hemp. Hemp sativa can produce many terpenes found in other plants. In the plant, they play a defensive role – they scare away potential pests. Terpenoids are oxidized forms of terpenes, formed during drying and extraction processes. Their action is more beneficial for the human organism than the action itself on the senses. They potentiate the effects of cannabinoids and can even stimulate cannabinoid receptors on their own. The diverse content of cannabinoids, especially terpenes, in individual varieties determines the specific effect of a given variety.
Entourage effect
This effect, otherwise known as the ambient effect, describes the mechanism by which individual compounds (cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids) act together more strongly, and often obtain additional properties through synergy. An example is limonene, which by influencing the conductivity in the central nervous system, affects the mood, reduces the feeling of anxiety and depression, which overlaps with the action of cannabinoids, and when combined with them – works more effectively.











