What is CBD?
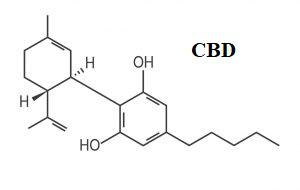
It is an abbreviation of cannabidiol - one of the main and most well-known phytocannabinoids. CBD has been known since 1940, though the first studies on its effects on the body appeared only in the 1970s. Its effects occur not only when it directly binds to cannabinoid receptors but also by affecting endocannabinoid metabolism, which boosts its natural levels.
Unlike its cousin THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), cannabidiol has no intoxicating effects and can either reduce or completely abolish these properties - important information for those wishing to enjoy the potential of cannabis without compromising psychomotor functions, or facing legal consequences.
Cannabidiol is naturally found in both cannabis and fibrous hemp in the form of CBD acid (CBDa), which is activated when exposed to high temperatures via decarboxylation.
CBD is a lipophilic compound, i.e. it dissolves in fats and, therefore, fats are an ideal carrier for it - one of them with special properties is the MCT oil (medium-chain fatty acids), which penetrate directly into the bloodstream from the digestive tract and do not participate in digestive processes, which also destroy cannabinoids. Although they are saturated fatty acids, in contrast to long-chain fatty acids, they do not increase the level of "bad" cholesterol.
Cannabidiol, like other cannabinoids, is sensitive to temperature and light. Therefore, the ideal places to store it would be cool and dark. Additionally, the carrier MCT oil slows down the oxidation processes mostly occurring when oils are stored for long periods.
Bibliografia:
Chung H, Fierro A, Pessoa-Mahana CD. Cannabidiol binding and negative allosteric modulation at the cannabinoid type 1 receptor in the presence of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol: An In Silico study. PLoS One. 2019;14(7):e0220025. Published 2019 Jul 23. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0220025
Casajuana Köguel C, López-Pelayo H, Balcells-Olivero MM, Colom J, Gual A. Psychoactive constituents of cannabis and their clinical implications: a systematic review. Adicciones. 2018 Apr 15;30(2):140-151. English, Spanish. doi: 10.20882/adicciones.858. PMID: 28492950.
Christian D. Schubart, Iris E.C. Sommer, Willemijn A. van Gastel, Rogier L. Goetgebuer, René S. Kahn, Marco P.M. Boks,nCannabis with high cannabidiol content is associated with fewer psychotic experiences,bSchizophrenia Research, Volume 130, Issues 1–3, 2011, Pages 216-221, ISSN 0920-9964,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2011.04.017.
Pavlovic R, Nenna G, Calvi L, Panseri S, Borgonovo G, Giupponi L, Cannazza G, Giorgi A. Quality Traits of “Cannabidiol Oils”: Cannabinoids Content, Terpene Fingerprint and Oxidation Stability of European Commercially Available Preparations. Molecules. 2018; 23(5):1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051230











