ECS endocannabinoid system
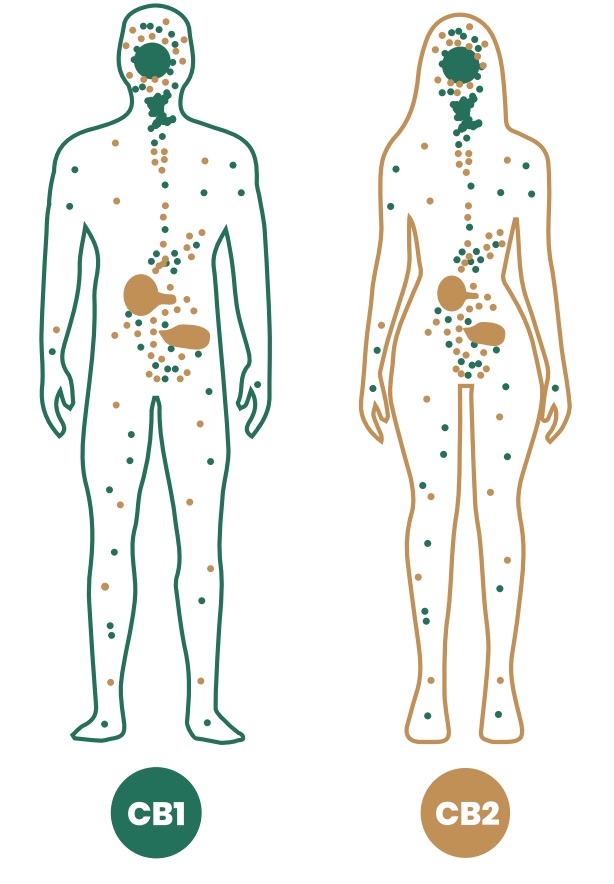
There are multiple systems in the human body. The endocannabinoid system is relatively recently recognized and is currently under intensive research. It consists of endocannabinoids produced by the organism - information carriers (key) - and receptors for them - prevalent are CB1 and CB2 receptors (lock), distributed throughout the body. The combination of the key and the lock causes a cascade of reactions between the cell and the desired response.
The receptor distribution determines the effect. CB1 receptors are mainly in the central and peripheral nervous systems. However, they are also abundant in fat and muscle tissue, liver cells and the gastrointestinal tract. CB2 is found mainly in immune-related tissues - tonsils, spleen, thymus - and on immune cells themselves - monocytes, B and T lymphocytes, macrophages. They also occur in the nervous system as well as the gastrointestinal tract.
Studies of ECS indicate that it participates in the regulation of the following processes:
- metabolic processes, e.g. hepatic
- digestion and appetite regulation
- cardiovascular system
- chronic pain
- inflammatory and immune system reactions
- stress response
- mood regulation
- learning and memory
- bone growth
- in the skin and nerves
- and many others
In conclusion, scientists consider the role of the endocannabinoid system to be fundamental in maintaining homeostasis of the body, i.e. maintaining a constant balance of all processes occurring within it.
Bibliografia:
1) Zou S, Kumar U. Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):833. Published 2018 Mar 13. doi:10.3390/ijms19030833
2) Pacher P, Bátkai S, Kunos G. The endocannabinoid system as an emerging target of pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58(3):389-462. doi:10.1124/pr.58.3.2
3) Gómez M, Hernández M, Fernández-Ruiz J. Cannabinoid signaling system: does it play a function in cell proliferation and migration, neuritic elongation and guidance and synaptogenesis during brain ontogenesis?. Cell Adh Migr. 2008;2(4):246-248. doi:10.4161/cam.2.4.6749
4) De Laurentiis A, et al. (2014). Role of the endocannabinoid system in the neuroendocrine responses to inflammation. DOI: 2174/1381612820666140130212957











